Introduction to the upright piano mechanism
The upright piano is a fascinating musical instrument that has captivated musicians and enthusiasts for centuries. It is known for its distinctive vertical design, which sets it apart from its counterpart, the grand piano.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the mysteries of the upright piano mechanism, uncovering its history, exploring its components, and understanding its intricate action.
History and evolution of upright pianos
The history of upright pianos can be traced back to the early 18th century when the first attempts to create a compact, vertical piano were made.
These early models were known as “upright harpsichords” and were the precursors to the modern upright piano. Over the years, advancements in technology and design led to the development of more refined and sophisticated upright pianos.
In the 19th century, the upright piano gained popularity due to its compact size and affordability. It became a staple in households and music schools, allowing more people to experience the joy of playing the piano.
The upright piano continued to evolve throughout the 20th century with the introduction of new materials and manufacturing techniques, further enhancing its sound and playability.
Components of the upright piano mechanism
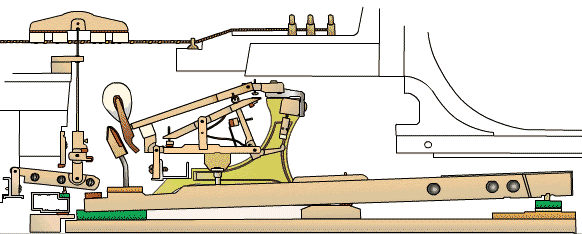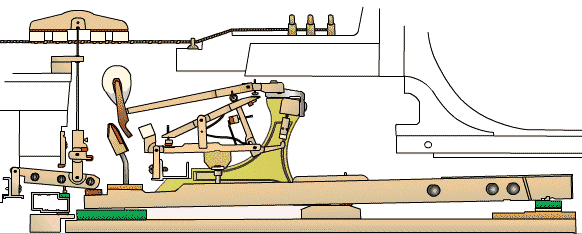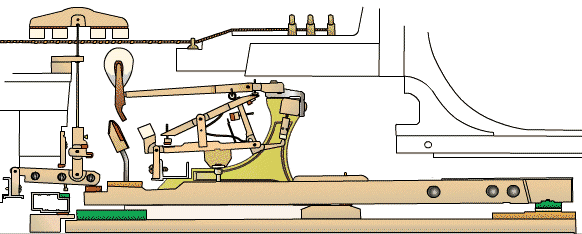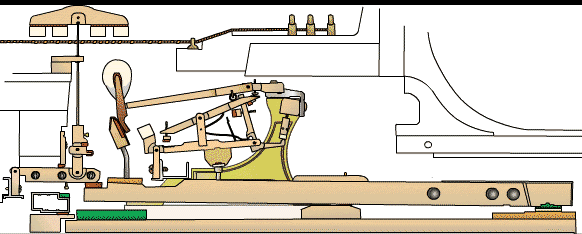
To understand the upright piano mechanism, it is important to familiarize yourself with its key components. The main parts of an upright piano include the soundboard, strings, bridges, hammers, dampers, keys, and pedals. Each component plays a crucial role in producing and controlling the sound of the instrument.
The soundboard is a large, wooden resonating surface that amplifies the vibrations of the strings, giving the piano its rich and resonant tone.
The strings are stretched across the soundboard and are responsible for producing the sound when struck by the hammers. The bridges transmit the vibrations from the strings to the soundboard, ensuring optimal sound transmission.
Understanding the action of an upright piano

The action of an upright piano refers to the mechanism that translates the motion of the keys into the striking of the strings by the hammers. The action consists of a series of levers, springs, and other mechanical parts that work together to ensure precise and responsive key movement.
When a key is pressed, it activates a series of levers and springs that cause the corresponding hammer to strike the string. The force with which the key is pressed determines the intensity of the sound produced. The action also includes a mechanism called the escapement, which allows the keys to be played rapidly without interfering with each other.
The role of the keys in the upright piano mechanism
The keys of an upright piano are the interface between the player and the instrument. They are the means by which the performer expresses their musical ideas and emotions. The keys are typically made of wood and are covered with a layer of ivory or synthetic materials for a smooth and comfortable playing experience.
Each key is connected to a corresponding hammer through a series of levers and pivots. When a key is pressed, it sets in motion a chain of events that ultimately leads to the striking of the string by the hammer. The length and weight of the keys are carefully designed to provide the player with optimal control and sensitivity.
The hammers and their importance in producing sound
The hammers are arguably the most critical components of the upright piano mechanism when it comes to sound production. They are responsible for striking the strings and creating the initial vibration that produces the sound. The hammers are typically made of wood and covered with layers of felt to produce a warm and mellow tone.
The shape, density, and resilience of the hammers have a significant impact on the overall sound of the piano. Well-maintained hammers will produce a clear and balanced tone, while worn-out or improperly shaped hammers can result in a dull or uneven sound.
Regular voicing and reshaping of the hammers are essential to maintain the optimal sound quality of the instrument.
Exploring the damper system in upright pianos
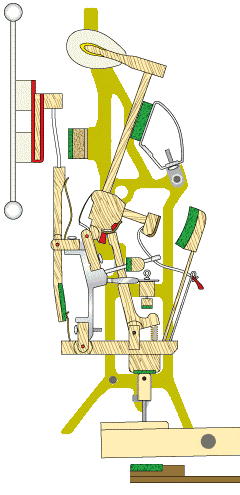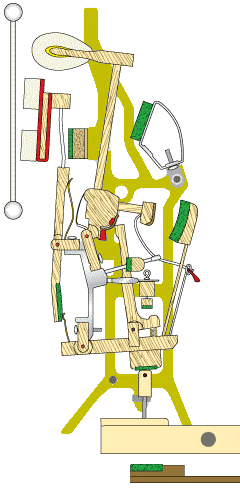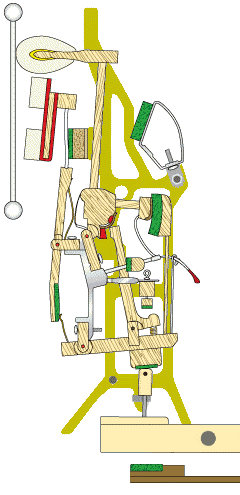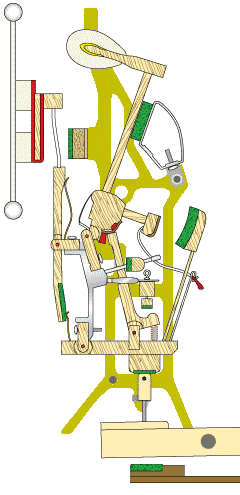
The damper system in an upright piano is responsible for controlling the duration of the sound produced. When a key is released, the dampers come into contact with the strings, stopping their vibrations and causing the sound to cease. The damper system ensures that only the intended notes are sustained while preventing unwanted sounds or overtones.
The damper system consists of a series of felt-covered levers that are activated by the keys. When a key is pressed, the damper for that particular string is lifted, allowing the string to vibrate freely.
When the key is released, the damper returns to its resting position, stopping the vibration of the string. Proper regulation and adjustment of the damper system are essential to ensure accurate and reliable damping.
Maintaining and troubleshooting the upright piano mechanism
Proper maintenance and regular servicing are essential to keep the upright piano mechanism in optimal condition. Regular cleaning and dusting of the keys and action components help prevent the buildup of dirt and debris, which can affect the performance and responsiveness of the instrument.
Regular tuning is also crucial to maintain the correct pitch and tonal balance of the piano. Changes in temperature and humidity can cause the strings to expand or contract, resulting in the piano going out of tune. A qualified piano technician can help you with the regular tuning and maintenance of your upright piano.
In case of any issues or problems with the upright piano mechanism, it is best to consult a professional piano technician. They have the expertise and knowledge to diagnose and repair any mechanical or technical problems. Attempting to fix the issues yourself may cause further damage to the instrument.
Differences between the upright piano mechanism and grand piano mechanism
While both the upright and grand pianos share similar principles in their mechanisms, there are some notable differences between the two. One of the primary differences is the orientation of the strings and soundboard. In an upright piano, the strings and soundboard are positioned vertically, while in a grand piano, they are horizontal.
The vertical orientation of the upright piano mechanism allows for a more compact design, making it suitable for smaller spaces. However, this design also affects the touch and feel of the keys. Grand pianos typically offer a more responsive and sensitive key action, allowing for greater control and expressiveness.
Conclusion and final thoughts
The upright piano mechanism is a complex and intricate system that brings the instrument to life. Understanding its history, components, and operation can deepen our appreciation for the instrument and enhance our playing experience. Regular maintenance and care are essential to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the upright piano mechanism.
Whether you are a professional pianist or an aspiring beginner, the upright piano offers a world of musical possibilities. By exploring its mysteries and mastering its mechanism, you can unlock the full potential of this remarkable instrument. So, let the music flow and embark on a journey of discovery with the upright piano mechanism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the mechanism of a piano called?
The mechanism of a piano is commonly referred to as the action. The action is the intricate system of levers, hammers, and other components that work together to produce sound when a key is pressed. It is essentially the heart and soul of the instrument, responsible for creating the beautiful tones that we associate with the piano.
The action consists of several key parts, including the keys themselves, the hammer mechanism, and the dampers. When a key is pressed, it sets off a chain reaction of events within the action. The key is connected to a series of levers that ultimately cause a hammer to strike the strings, producing sound.
At the same time, the dampers are lifted off the strings to allow the sound to ring out. This entire process happens in a fraction of a second, allowing the piano to produce a sustained and resonant sound.
In addition to the keys, hammers, and dampers, the action also includes other components such as springs, felt, and wooden parts. Each part is carefully crafted and adjusted to ensure optimal performance and responsiveness. The mechanism of a piano is a marvel of engineering, designed to translate the pianist’s touch into music.
What are the different types of upright piano actions?
Upright pianos, also known as vertical pianos, come in various sizes and designs, each with its own unique action mechanism. The two main types of upright piano actions are the direct blow and indirect blow actions.
The direct blow action is the most common type found in modern upright pianos. In this design, the keys are connected directly to the hammers, which strike the strings when the keys are pressed.
The hammers are positioned vertically, allowing them to strike the strings from below. This direct connection between the keys and hammers results in a more immediate and responsive touch, making it easier for the pianist to control the dynamics and expression of their playing.
On the other hand, the indirect blow action is a less common design that is typically found in older upright pianos. In this action, the keys are connected to a series of levers and rods that transmit the motion to the hammers.
The hammers, in turn, strike the strings from the side rather than from below. This indirect connection between the keys and hammers can result in a slightly different feel and touch compared to the direct blow action.
Both types of upright piano actions have their own unique characteristics and advantages. The choice between them ultimately depends on the pianist’s personal preference and playing style.
What is the upright piano repetition mechanism?
The repetition mechanism is a crucial component of an upright piano action that allows for rapid and repeated playing of the same note. It is designed to ensure that the hammer returns to its original position quickly after striking the string, allowing for the immediate repetition of the note without any delay.
In an upright piano, the repetition mechanism is achieved through the use of a lever called the repetition lever. When a key is pressed, the repetition lever is activated, causing the hammer to be released from the string and then quickly reset.
This rapid resetting of the hammer allows for the quick repetition of the note, enabling the pianist to play fast and intricate passages with ease.
The repetition mechanism is a testament to the ingenuity and craftsmanship that goes into the design of an upright piano action. It is a delicate balance of mechanical precision, ensuring that the piano responds accurately and reliably to the pianist’s touch.
Why is it called upright piano?
The term “upright piano” is used to describe a specific type of piano that is vertically oriented, as opposed to a grand piano, which has a horizontal orientation. The name “upright” refers to the fact that the strings and soundboard of the piano are positioned vertically, with the strings running perpendicular to the keyboard.
The upright piano was developed as a more compact and space-saving alternative to the grand piano. Its vertical design allows it to take up less floor space, making it ideal for smaller rooms and homes. Additionally, the vertical orientation of the strings and soundboard creates a different tonal quality compared to a grand piano, with a more focused and direct sound.
Despite its smaller size, the upright piano is capable of producing a rich and resonant sound. Its upright design also offers other advantages, such as easier maintenance and accessibility for tuning and repairs. The term “upright piano” has become the standard way to refer to this type of instrument, distinguishing it from other types of pianos.
How does a mechanical piano work?
A mechanical piano, also known as a player piano, is a type of upright piano that has the ability to play music on its own. It is equipped with a mechanism that allows it to reproduce music recorded on perforated paper rolls or, more recently, digital files.
The mechanism of a mechanical piano consists of a series of pneumatic devices and levers that are controlled by the paper roll or digital file. When the piano is in player mode, the mechanism activates the keys and pedals, causing them to be played as if by an invisible pianist.
The player mechanism works by using suction or pressure to operate the keys and pedals of the piano. When a hole in the paper roll or a digital command is detected, the corresponding pneumatic device is activated, causing the key or pedal to be pressed.
This process is synchronized with the timing and dynamics of the music, allowing the piano to accurately reproduce the original performance.
Mechanical pianos have been around for over a century and have played a significant role in the history of music. They have provided a means for people to enjoy live music in their own homes, even if they don’t know how to play the piano themselves.
What is an upright piano that plays itself?
An upright piano that plays itself is a type of mechanical piano that is capable of reproducing music without the need for a pianist. It is equipped with a player mechanism that activates the keys and pedals, allowing it to play music recorded on perforated paper rolls or digital files.
The self-playing mechanism of an upright piano is similar to that of other mechanical pianos. It consists of a series of pneumatic devices and levers that are controlled by the paper roll or digital file. When the piano is in player mode, the mechanism reads the perforations on the paper roll or the digital commands, activating the corresponding keys and pedals.
The ability of an upright piano to play itself offers a unique and convenient way to enjoy live music. It allows for the reproduction of complex and virtuosic performances that would otherwise be difficult for an average pianist to play.
With the advancements in technology, self-playing upright pianos can now even connect to the internet, providing access to a vast library of recorded performances.
Whether used for entertainment or as a learning tool, an upright piano that plays itself adds a new dimension to the enjoyment of music. It allows anyone to experience the beauty and artistry of piano music, even if they don’t know how to play the instrument.
How does a simple piano work?
A simple piano, also known as a toy piano or a miniature piano, is a smaller version of a traditional upright or grand piano. It is designed to be accessible and easy to play, making it a popular choice for children and beginners.
Despite its smaller size and simplified design, a simple piano works on the same basic principles as a full-sized piano. It consists of a keyboard with keys that are connected to hammers, which strike metal or plastic bars to produce sound.
In a simple piano, the keys and hammers are typically made of lightweight materials to make them easier to play. The sound produced is also softer and more muted compared to a full-sized piano. This allows for a gentler and less intimidating playing experience for young children or those who are just starting to learn the piano.
Simple pianos are often used as an introductory instrument for children to develop their sense of pitch, rhythm, and musicality. They provide a stepping stone to more advanced pianos and can serve as a fun and engaging tool for learning the basics of music.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mechanism of an upright piano, also known as the action, is a complex and intricate system of levers, hammers, and other components that work together to produce sound.
The different types of upright piano actions, such as the direct blow and indirect blow actions, offer unique characteristics and advantages. The repetition mechanism ensures rapid and repeated playing of the same note.
The term “upright piano” is used to describe the vertical orientation of the instrument, which allows for a more compact design and a different tonal quality compared to a grand piano.
Mechanical pianos, including upright pianos that play themselves, rely on a player mechanism to reproduce music recorded on perforated paper rolls or digital files. Simple pianos offer a smaller and simplified version of the piano, making it accessible and easy to play for beginners.
Understanding the mechanism and different types of upright pianos can deepen one’s appreciation for this beautiful instrument. Whether you are a pianist, a music enthusiast, or simply curious about the inner workings of a piano, exploring these frequently asked questions provides valuable insights into the world of upright pianos.
- Yuja Wang Family – All There is To Know! - June 4, 2024
- Top 10 Adjustable Piano Chairs in 2024 - June 2, 2024
- The 10 Most Popular Types of Jazz Piano You Need to Check Out! - May 31, 2024